Modes of Heat Transfer
The movement of thermal energy between systems can take place in one of four modes, where energy is transferred as heat flows from the higher-temperature object to the lower-temperature object. In most cases, two or more types of heat transfer are active at the same time, depending on whether the objects involved are touching, surrounded by a fluid, or visible to one another.
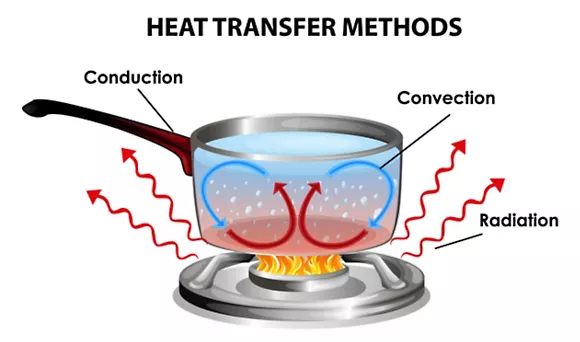
Here is a brief definition of each mode.
Advection
Thermal advection is the mechanism of thermal energy transfer where heat is transported from one location to another through the motion and momentum of a fluid. Advection is sometimes referred to as forced convection to differentiate it from the strict definition of convection because the fluid flow in advection is not caused by buoyancy forces but instead is imparted by adding energy to the system.
A fan cooling a computer motherboard is an example of advective heat transfer.
Thermal Conduction
Thermal conduction describes the transfer of heat between two objects in direct contact or within an object with a temperature difference across the object. It describes the transfer of energy through thermal diffusion as described in Fourier's law for heat conduction. The speed of energy transfer is driven by the thermal conductivity of the material and the temperature gradient in the object or objects. For two objects in physical contact, the pressure and fit between the two surfaces determines the thermal contact resistance.
An example of thermal conduction is the handle on a pot on a stove. Heat moves from the pot's base up its walls and into the handle.
Convection
Convection, or convective heat transfer, is the transfer of thermal energy due to the motion of a fluid driven by buoyancy caused by temperature differences in the fluid. Engineers generally refer to it as free convection or natural convection to differentiate it from advection or forced convection.
A common example of convection is simply leaving a mug of hot coffee or tea sitting out. The warm drink transfers heat into the air, and buoyancy forces carry the heat away.
Radiation
Radiation heat transfer is a mechanism that transfers heat energy as electromagnetic waves/photons. Thermal energy causes the atoms in any form of matter to move, and the movement of the charged particles in those atoms (protons and electrons) results in the emission of electromagnetic radiation. Heat transfer due to thermal radiation only occurs in a vacuum or through a medium that is transparent to the infrared wavelengths emitted due to an object's temperature.
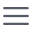
For the heat transter from the CPU to the cooler, it is Thermal conduction mode. Becasue higher power of the devices but smaller area for thermal conduction, higher request for thermal interface materials(TIM) now. We are thermal paste, thernal putty manufacturer in China over 16 years, cost effective & extreme performance products are available.

 中文
中文

.png) Search
Search

 >
>  Return to List
Return to List